
Abhyanga Snanam – Ayurveda’s take
For many out there Diwali is the festival of lights. But If you ask me what is Diwali, I would say “Diwali is a wisely

Pregnancy is worth celebrating. The journey of bringing a new life to the world is an ensemble package of happiness, nervousness, pampering, worrying, caring, wondering, dreaming, and not forgetting the physical discomfort. With science reaching newer heights every day, some of these worries are pacified and some of these curious questions are answered. Making this beautiful natural process much more healthy, fruitful, and predictable is what science is striving for.
Its human tendency to be positive. But one must not forget to see both sides on a coin. There are multiple possibilities about pregnancy going wrong or child getting affected or a child born with genetic abnormalities, one of such abnormalities is Down syndrome.
Chromosomes are a threadlike structure of nucleic acids and proteins that carry information in the form of genes. They are passed down from parent to child and that’s how heredity works. They carry information that determines a child’s unique traits like eye color, height, etc.
People normally have 46 chromosomes in each cell, i.e. 23 pairs. Each pair consisting two chromosomes, one from each parent.
Down syndrome is a chromosomal abnormality wherein an individual has 47 chromosomes in each cell instead of 46. This is caused by an error in cell division. Following are causes of Down syndrome –
1. Trisomy 21
It is caused when abnormal cell division development of the sperm cell or the egg cell results in an extra full or partial copy of chromosome 21. Here the child has three copies of chromosome 21, instead of the usual two copies, in all cells. In 95% of cases, Down syndrome is caused by trisomy 21.
2. Mosaic Down syndrome
Here the child has some cells with an extra copy of chromosome 21, while some cells have regular two chromosomes. This mosaic of normal and abnormal cells is caused by abnormal cell division after fertilization. Mosaic Down syndrome is a rare phenomenon.
3. Translocation Down syndrome
Here a portion of chromosome 21 becomes attached (translocated) onto another chromosome, before or at conception. The child has usually two copies of chromosome 21 but also has additional genetic material from chromosome 21 attached to other chromosomes.
Down syndrome cannot be treated, and the child suffers from mental retardation along with few physical disabilities like Heart defects, Gastrointestinal defects, Immune disorders, Sleep apnea, Obesity, Spinal problems, Leukemia, Dementia, endocrine problems, dental problems, seizures, ear infections, hearing, vision problems, etc.
The extra chromosome changes the way of body and brain development.
Advancing maternal age has a high chance of Down syndrome as the older eggs have a greater risk of improper chromosome division. Mostly the pregnant women above 25 years of age should get this test done.
If you have already had a baby with Down syndrome or have a family history of the disorder, you may be at higher risk.
If the result is positive, you can take your big decisions and can prepare yourself mentally and physically. Knowing in advance can give you time to plan for further health care, treatments, support services for your child and family.
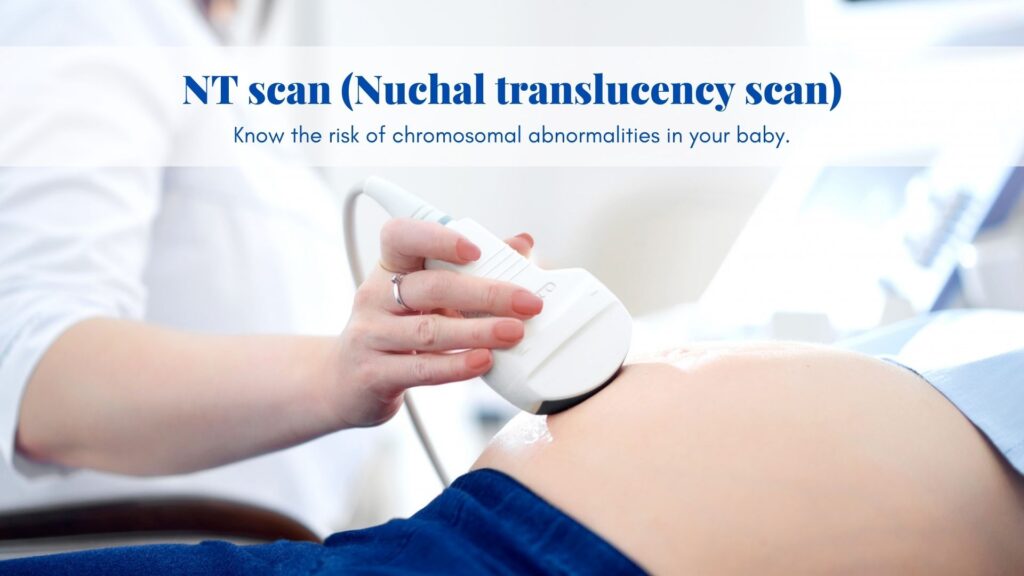
Double marker test or Down syndrome screening diagnoses and gives the result considering blood test, mother’s age, and USG parameters specifically NT i.e Nuchal translucency which means the thickness of the skin at the neck of the baby. This test is done to screen the possibility of a potential abnormal baby.
The blood sample is taken to measure the levels of free Beta HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) and PAPP-A (pregnancy-associated plasma protein) both are the hormones produced by the placenta.
High levels of HCG and low levels of PAPP-A can be associated with Down syndrome along with the combining USG parameters.
Results are represented as screen positive, high risk, or screen negative.
This test should be done in between 11-14 weeks and if missed due to any reason then can be done in between 16-22 weeks.
Along with Trisomy 21 Down syndrome, the Dual marker test helps to detect Trisomy 18 i.e. Edward syndrome, and Trisomy 13 i.e. Patau syndrome.
Edward syndrome- Heart defects, low birth weight, abnormal shape head, small jaw, clenched hand, and mental disabilities.
Patau syndrome – Physical defects like cleft palate, cleft lip, convex foot, extra fingers or toes, and mental disabilities too.
If the Dual marker test is positive, a further diagnostic test called “amniocentesis” is advised at 16 weeks to confirm the diagnosis.
Blog ends.
Are you pregnant? Don’t forget to check out blog on Garbhasamvad. A special Ayurvedic practice to bond with your child.

For many out there Diwali is the festival of lights. But If you ask me what is Diwali, I would say “Diwali is a wisely

As the best parent, everyone tries to protect their child in all possible ways. Our parents did the same to us and still do it.

Besides being a Doctor, like every other pregnant woman I too had a lot of confusion regarding what essentials I should have to make my
As a mother, I always had a hundred thoughts in my mind during my pregnancy. I always wanted to be sure about whether my baby

Are you dealing with stress in pregnancy? Have you ever desired for a quick and easiest remedy to charge you up in those depressed and

At their core, traditional recipes are a way of ensuring you’re eating what your body needs to stay healthy and feeling good. Each recipe has
Copyright © 2021 truptwellness | Powered by truptwellness
Any questions? Click for Consultation.
2 Responses